GENESIS Tutorial 3.3 (2022)
MD simulation of Protein G in NaCl solution
Preparation
All the files required for this tutorial are hosted in the GENESIS tutorials repository on GitHub.
If you haven’t downloaded the files yet, open your terminal and run the following command:
# if not yet
$ git clone https://github.com/genesis-release-r-ccs/genesis_tutorial_materials
This tutorial consists of five steps: 1) system setup, 2) energy minimization, 3) equilibration, 4) production run, and 5) trajectory analysis. The control files for GENESIS are already included in the download file. To use the CHARMM36m force field parameters 1, we create a symbolic link to the CHARMM toppar directory (see Tutorial 2.2).
# If you already have the tutorial materials, let's go to our working directory:
$ cd genesis_tutorial_materials
# Let's take a note
$ echo "tutorial-3.3: MD simulation of Protein G in NaCl solution" >> README
# Check the contents of Tutorial 3.3
$ cd tutorial-3.3
$ ln -s ../../Data/Parameters/toppar_c36_jul21 ./toppar
$ ln -s ../../Programs/genesis-2.0.0/bin ./bin
$ ls
1_setup 3_equilibrate 5_analysis bin
2_minimize 4_production benchmark toppar
One of the aims of this tutorial is to help you think about how to
perform efficient calculations. To do this, we first need to know the
architecture of the CPU in the computer in advance. We assume that you
are using a typical Linux workstation. Let’s review the CPU information
on the computer. You can use the following command (or the lscpu command) to know the CPU model, number of physical CPUs, number of cores
in one physical CPU, and number of logical processors.
# Check the CPU model
$ grep 'model name' /proc/cpuinfo | uniq
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2670 0 @ 2.60GHz
# Check the number of physical CPUs
$ grep physical.id /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u | wc -l
2
# Check the number of cores in one physical CPU
$ grep cpu.cores /proc/cpuinfo | sort -u
cpu cores : 8
# Check the number of logical processors
$ grep processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
16
This example shows that the computer is equipped with an Intel Intel Xeon E5-2670 processor. There are two physical CPUs, each of which has 8 CPU cores. Thus, there are 16 CPU cores in total. This CPU architecture can be pictured as follows. Please try to draw a similar picture for your case.
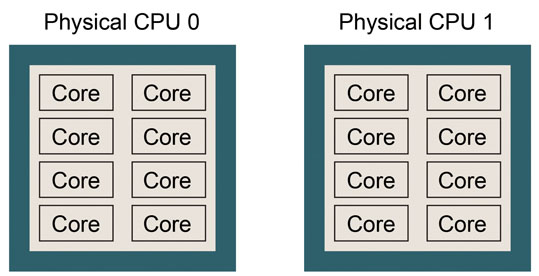
If number of logical processors is twice the (number of physical CPUs) * (number of cores in one physical CPU), hyper-threading might be turned on, which means that the number of logical processors is virtually doubled. If so, performance of GENESIS may suffer. Please consult with the system administrator if you want to disable the hyper-threading.
1. Setup
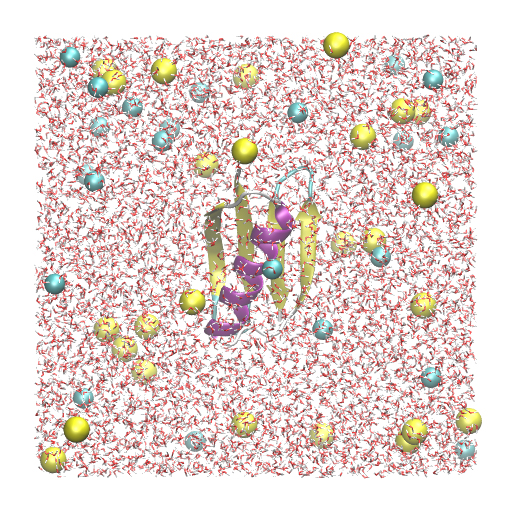
In this tutorial, we will simulate protein G using the all-atom model.
The detailed setup scheme of the system has already been described in
Tutorial 2.3
and will not be covered here. Since we will create symbolic links to the
files and directories obtained in Tutorial 2.3, please
finish that first, if you have not yet done. The protein is solvated in
a 150 mM NaCl solution with a box size of 64 Å × 64 Å × 64 Å, resulting
in a total number of 24,552 atoms in the system. We have ionized.pdb
and ionized.psf as input files for GENESIS. Since the system is twice
as large as in Tutorial 3.2, there will be much computational cost for the MD
simulation.
# Change directory for the system setup
$ cd 1_setup
$ ln -s ../../tutorial-2.3/* ./
$ ls
1_oripdb 2_modpdb 3_psfgen 4_solvate 5_ionize toppar
$ ls ./5_ionize
build.tcl ionized.pdb ionized.psf log
2. Minimization
First, we perform a 2,000-step energy minimization with the steepest
descent (SD) method. We use the CHARMM C36m force field parameters. The
particle mesh Ewald method (PME) 2 is used to compute the long-range
interactions. The scheme is the same as in Tutorial 3.2. Let’s
execute spdyn for the control file INP. The following command uses 4
MPI processors and 4 OpenMP threads, that is, a total of 16 CPU cores.
It will take about 1 minute to finish the calculation.
# Change directory for the energy minimization
$ cd ../2_minimize
# Run energy minimization
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP > log
# Check the log output
$ less log
Now, let’s check the log file. At the end of the file, you will
recognize that “ring structure” and “chirality” are checked for the
energy-minimized structure. In this case, we could not find any
suspicious residues that may contain ring penetration or chirality
error. However, such errors are rarely found even in the system that was
minimized from the high-resolution X-ray crystal structure, and you have
to pay attention to the results of this error check for every case.
GENESIS checks those errors in general amino acids and nucleic acids.
For details, see the user manual ([MINIMIZE] section) or Tutorial Appendix 6.
:
Check_Ring_Structure> Check ring structure
No suspicious residue was detected.
Check_Chirality> Check chirality
No suspicious residue was detected.
:
3. Equilibration
The system is gradually equilibrated in three steps as in Tutorial 3.2. First, we perform a 50-ps MD simulation with positional constraints on the heavy atoms of the protein (force constant = 1.0 kcal/mol/Å2) in the NVT ensemble at T = 298.15 K. The equations of motion are integrated with a time step of 2 fs with the velocity Verlet algorithm, in which the SHAKE/RATTLE 3,4 and SETTLE 5 algorithms are used for the bond constraint. The temperature is controlled with the Bussi thermostat 6. Then, we perform a 50-ps MD simulation in the NPT ensemble at T = 298.15 K and P = 1 atm with the Bussi thermostat and the barostat 7. Positional restraints are applied to the protein backbone heavy atoms. The other simulation conditions are the same as in the first step. Finally, we perform a 50-ps MD in the NPT ensemble at T = 298.15 K and P = 1 atm , where the equations of motion are integrated with the RESPA algorithm 8 with a time step of 2.5 fs. In the RESPA integrator, the PME calculation is performed every 2 steps and the thermostat and ballostat momenta are updated every 10 steps.
# Change directory for equilibration
$ cd ../3_equilibrate
# Step1: NVT-MD with positional restraints on protein heavy atoms
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP1 > log1
# Step2: NPT-MD with positional restraints on protein heavy atoms
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP2 > log2
# Step3: NPT-MD with positional restraints on protein backbone heavy atoms
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP3 > log3
4. Production
Benchmark test
Now, before we go into the production run, let’s check the benchmark performance of GENESIS. Of course, if many CPU cores are available, you can expect that the simulation will finish quickly. Benchmark test will give you detailed information in advance on how many hours or days the simulation will take to finish.
# Change directory for benchmark check
$ cd ../benchmark
$ ls
INP
In the benchmark test, we measure the simulation time by changing the
number of CPU cores. Our computer has 16 CPU cores as shown above.
Therefore, in the following commands, we measure the time using 1, 2, 4,
8, and 16 CPU cores with various combinations of the number of MPI
processors and OpenMP threads. For example, in the case of 2 MPI x
2 OpenMP, 4 CPU cores are used, and in the case of 4 MPI x 4 OpenMP, 16 CPU
cores are used. Here, OpenMP is a thread-parallel computing scheme, in
which shared memory-based calculation is carried out. It performs well
within one physical CPU. Thus, the number of OpenMP threads
(OMP_NUM_THREADS) is basically set less than or equal to the number of
cores within one physical CPU. Please adjust the number of CPU cores
according to your computer environment. Each run is just a 1,000-steps
MD (2.5 ps), which is long enough to check the performance.
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=1
$ mpirun -np 1 ../bin/spdyn INP > 1MPIx1OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 2 ../bin/spdyn INP > 2MPIx1OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP > 4MPIx1OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP > 8MPIx1OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 16 ../bin/spdyn INP > 16MPIx1OpenMP
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=2
$ mpirun -np 1 ../bin/spdyn INP > 1MPIx2OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 2 ../bin/spdyn INP > 2MPIx2OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP > 4MPIx2OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP > 8MPIx2OpenMP
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
$ mpirun -np 1 ../bin/spdyn INP > 1MPIx4OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 2 ../bin/spdyn INP > 2MPIx4OpenMP
$ mpirun -np 4 ../bin/spdyn INP > 4MPIx4OpenMP
When using 16 MPI processors, the simulation was interrupted and the following error message was displayed:
Setup_Processor_Number> Cannot define domains and cells.
Smaller or adjusted MPI processors, or shorter pairlistdist,
or larger boxsize should be used.
This message indicates that 16 MPI processors cannot be used for this
calculation. SPDYN uses a method in which the system is divided into
multiple domains for parallel computation (domain decomposition scheme),
where the number of domains must be equal to the number of MPI
processors (for details, see the “Available Programs” chapter of the User Manual). This message tells you that the system could not be
divided into 16 domains. In fact, the domain size is related to the pair
list distance. If a short pairlistdist is specified in the control
file, it may be possible to divide the system into 16 domains. However,
since switching, cutoff, and pairlist distance are recommended at 10.0,
12.0, and 13.5, respectively, these should essentially remain unchanged.
Thus, in most cases, the above error message indicates that the “maximum
number of available MPI processors” has been reached.
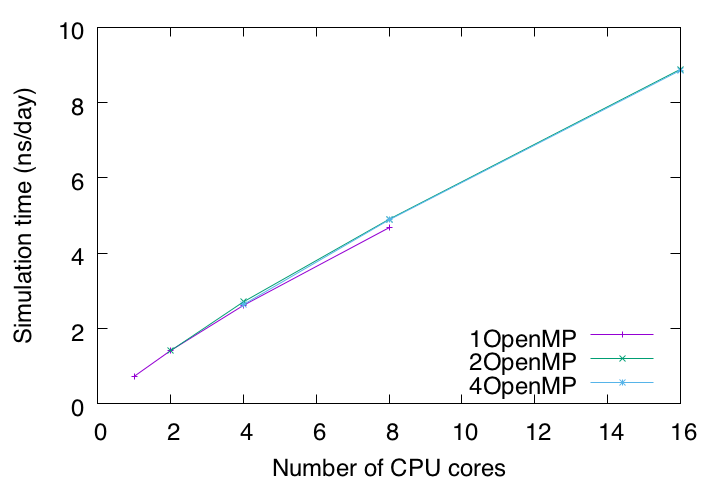
Now let’s collect the timings (timers for dynamics calculations) from all log files. Timers are in seconds. On our computer, we found that the best performance is achieved with 8 MPI processors and 2 OpenMP threads.
# Gather the timing from all log files
$ grep "dynamics =" * | sort -g -r -k 4 > timer.out
$ tail -4 timer.out
2MPIx4OpenMP: dynamics = 44.213
4MPIx2OpenMP: dynamics = 44.069
4MPIx4OpenMP: dynamics = 24.393
8MPIx2OpenMP: dynamics = 24.318
Since we ran a 2.5 ps MD simulation for each job, the timings (s/2.5 ps) are converted to ns/day with the following command.
# Convert sec/2.5ps to ns/day
$ awk '{print $1, 24*60*60*2.5*0.001/$4}' timer.out > benckmark.out
$ tail -4 benckmark.out
2MPIx4OpenMP: 4.88544
4MPIx2OpenMP: 4.9014
4MPIx4OpenMP: 8.855
8MPIx2OpenMP: 8.88231
To summarize, let’s plot the timings with the number of CPU cores on the X axis and the estimated simulation time (ns/day) on the Y axis. Currently, for all-atom MD simulations with explicit solvent, 1 μs or longer is the typical length of time. According to this benchmark test, it takes about 114 days to run a 1 μs MD simulation on this computer. Such an estimate is important for making a schedule and plan to complete the simulation within a limited research period.
File size estimation
Since MD simulations generate a large amount of trajectory data, but at the same time the available disk space is finite, it is important to estimate the file size of the MD trajectory data before the production runs. In a DCD file, the coordinates of atoms are written in single-precision floating-point numbers, consuming 4 bytes x 3 = 12 bytes per atom. Now the system has 24,552 atoms. Therefore, if the MD simulation outputs 50 frames, the size of the DCD file would be approximately 15 MB (24,552 x 50 x 12 bytes). In fact, the previous step of the equilibration run generated 15 MB of data at each stage. Based on this scheme, let us estimate the file size of the trajectory data generated in the subsequent production runs.
$ du -h ../3_equilibrate/*.dcd
15M ../3_equilibrate/eq1.dcd
15M ../3_equilibrate/eq2.dcd
15M ../3_equilibrate/eq3.dcd
Production run
Now let’s perform the production run. The simulation conditions are the
same as for the last stage of the equilibration run in Step 3, but with
the position restraints turned off. Here we use 8 MPI processors and 2
OpenMP threads to achieve the best performance. We run spdyn
sequentially for INP1–INP5, each corresponding to a 100-ps MD
simulation. In total, we will get 500-ps MD trajectories.
# Change directory for production run
$ cd ../4_production
$ ls
INP1 INP2 INP3 INP4 INP5
# Production runs
$ export OMP_NUM_THREADS=2
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP1 > log1
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP2 > log2
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP3 > log3
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP4 > log4
$ mpirun -np 8 ../bin/spdyn INP5 > log5
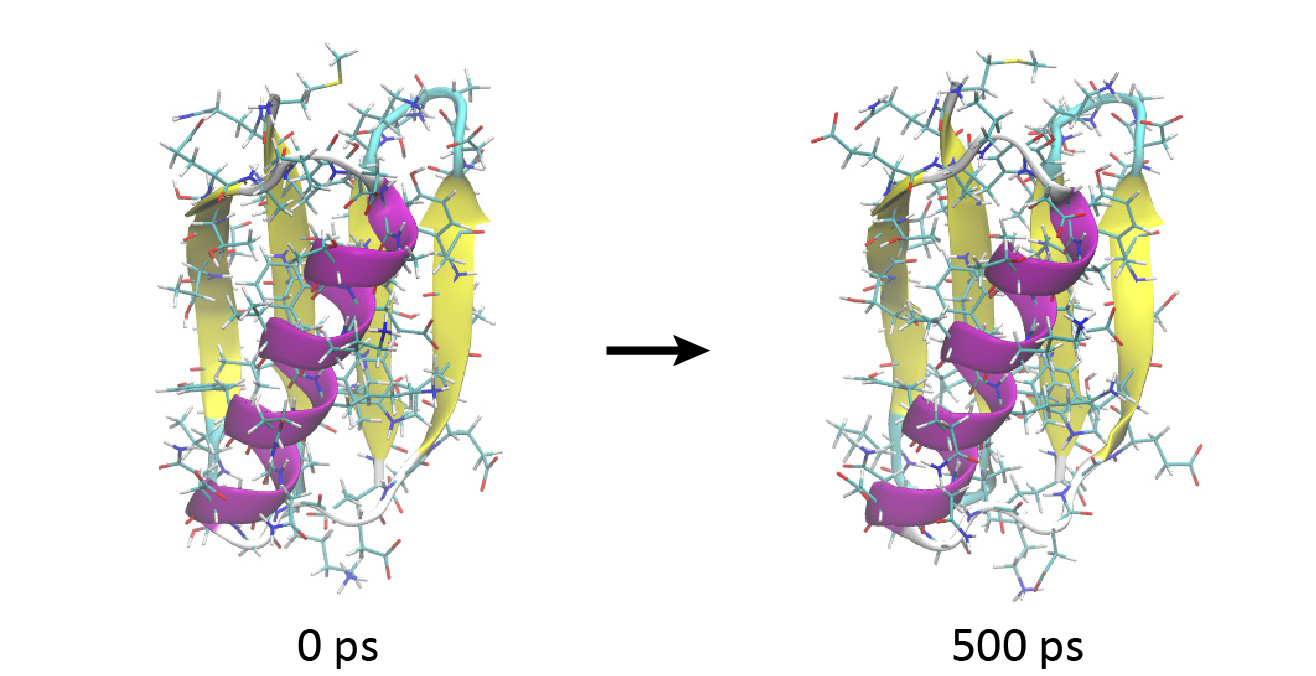
# View the MD trajectories using VMD
$ vmd ../1_setup/5_ionize/ionized.pdb -psf ../1_setup/5_ionize/ionized.psf -dcd md{1..5}.dcd
Looking at the trajectory, you will observe that the protein is very stable and does not show a large conformational change during 500 ps.
5. Analysis
In this section, we will mainly learn how to process coordinates trajectory files for efficient analysis. We will also analyze the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) of the protein using the processed DCD files.
# Change directory for analysis
$ cd ../5_analysis
$ ls
1_crd_convert_wrap 2_crd_convert_pro 3_rmsd
5.1 Make a trajectory file with PBC wrapping
When we load the coordinates trajectory data in VMD, we see that water
molecules are spread out of the box and the protein is undergoing
translational and rotational motions. This is a bit inconvenient for
trajectory analysis. By using the “crd_convert” tool in the GENESIS
program package, such trajectories can be converted to those in which
all molecules are wrapped into the unit cell and the target protein is
fitted to the original position.
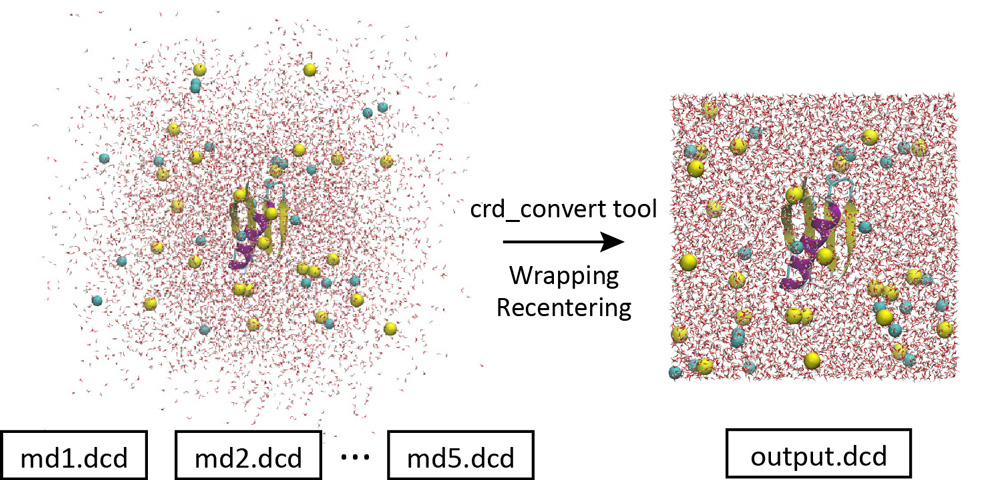
Let’s change the directory to “1_crd_convert_wrap” for this process.
This directory already contains the control file. The most important
part of the control file is shown below. When you convert the
trajectory, the center of mass of the protein is moved to the origin
(blue option) and all molecules are wrapped into the unit cell (red option). Here, psffile must be specified in the [INPUT] section for
the CHARMM force field to wrap the molecules. The coordinates of all
atoms in the system are output to a new DCD file “output.dcd” (green option). In the original 5 DCD files, there were a total of 1,000
snapshots (200 snapshots in each). To reduce the file size, the
trajectory analysis period is set to 800 instead of the original
crdout_period (purple option). Thus, the new DCD file contains a total
of 250 snapshots.
[INPUT]
psffile = ../../1_setup/5_ionize/ionized.psf # protein structure file
reffile = ../../1_setup/5_ionize/ionized.pdb # PDB file
[OUTPUT]
pdbfile = output.pdb # PDB file
trjfile = output.dcd # trajectory file
[TRAJECTORY]
trjfile1 = ../../4_production/md1.dcd # trajectory file
:
trjfile5 = ../../4_production/md5.dcd # trajectory file
md_step1 = 40000 # number of MD steps
mdout_period1 = 200 # MD output period (crdout_period)
ana_period1 = 800 # analysis period
repeat1 = 5
[SELECTION]
group1 = sid:PROA # selection group 1
group2 = all # selection group 2
[OPTION]
centering = YES # shift center of mass
centering_atom = 1 # atom group
center_coord = 0.0 0.0 0.0 # target center coordinates
pbc_correct = MOLECULE # (NO/MOLECULE)
trjout_format = DCD # (PDB/DCD)
trjout_type = COOR+BOX # (COOR/COOR+BOX)
trjout_atom = 2 # atom group
Let’s run crd_convert and check the resulting DCD file in VMD. This
DCD file is actually useful for analyzing protein-water interactions.
This is because in the original DCD file, many water molecules are
spread out of the box and present in the image cells, and we do not know
which water molecules are interacting with the protein. But with this
new DCD, it is obvious at a glance.
# Convert the trajectory (wrap molecules)
$ ../../bin/crd_convert INP > log
$ ls
INP log output.pdb output.dcd
# Check the trajectory using VMD
$ vmd output.pdb -dcd output.dcd
5.2 Make a trajectory file containing protein only
With crd_convert, it is possible to fit the Cα atoms to the initial
structure, remove the water molecules, and create a new DCD file
containing only protein atoms.
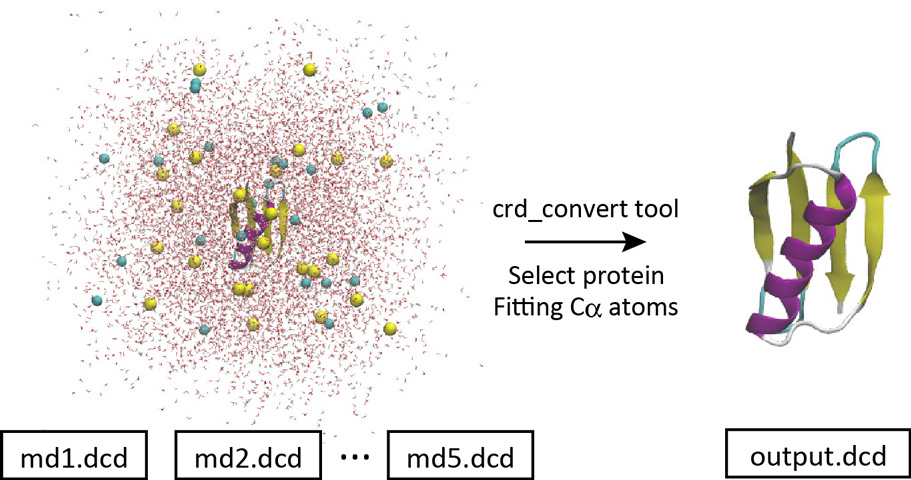
Let’s change the directory to “2_crd_convert_pro”. This directory
already contains the control file. Below is the most important part of
the control file. We select the protein atoms (red option) and write
them to a new DCD file (output.dcd) with the Cα atoms fitted to the
initial coordinates (ionized.pdb) by rigid-body translation and
rotation (TR+ROT) (blue option). Since all snapshots in the original 5
DCD files were analyzed, each of which contains 200 snapshots, the
resulting new DCD file contains 1,000 snapshots.
[SELECTION]
group1 = an:CA # selection group 1
group2 = sid:PROA # selection group 2
[FITTING]
fitting_method = TR+ROT # NO/TR+ROT/TR/TR+ZROT/XYTR/XYTR+ZROT
fitting_atom = 1 # atom group
[OPTION]
trjout_format = DCD # (PDB/DCD)
trjout_type = COOR+BOX # (COOR/COOR+BOX)
trjout_atom = 2 # atom group
Let’s run crd_convert and check the resulting DCD file in VMD. This
file is actually useful for analyzing the protein structure itself. This
is because for such a purpose we do not need the coordinates of water
molecules around the protein. In the original system, there were many
water molecules. If the original DCD files were used for the trajectory
analysis, it would take a very long time to just read in the coordinates
of the water molecules, which would be a waste of time. In the next
section, we will analyze the RMSD using the resulting DCD file instead
of using the original DCD files.
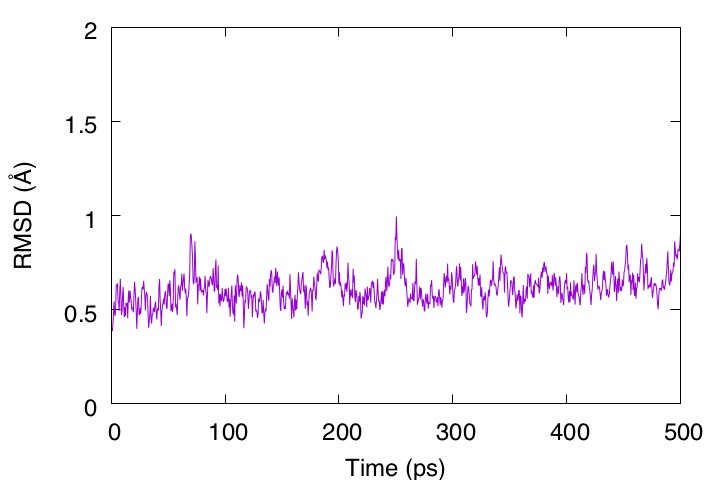
5.3 Root-mean-square deviation (RMSD)
To examine the structural stability of the protein, the rmsd_analysis
tool in GENESIS is used to analyze the RMSD of the Cα atoms with respect
to the initial structure. The DCD file obtained in the previous
subsection is used. In the analysis, each snapshot is fitted to the
initial structure (../2_crd_convert_pro/output.pdb) using rigid body
translation and rotation (TR+ROT).
[INPUT]
reffile = ../2_crd_convert_pro/output.pdb # PDB file
[TRAJECTORY]
trjfile1 = ../2_crd_convert_pro/output.dcd # trajectory file
md_step1 = 1000 # number of MD steps
mdout_period1 = 1 # MD output period
ana_period1 = 1 # analysis period
repeat1 = 1
:
[SELECTION]
group1 = an:CA # selection group 1
[FITTING]
fitting_method = TR+ROT # NO/TR+ROT/TR/TR+ZROT/XYTR/XYTR+ZROT
fitting_atom = 1 # atom group
[OPTION]
analysis_atom = 1 # atom group
During 500 ps, the RMSD is less than 1 Å, indicating that this protein structure is very stable. However, the RMSD is still gradually increasing and may require longer simulation runs to converge.
Written by Takaharu Mori@RIKEN Theoretical molecular science
laboratory
March 8, 2022
References
-
Huang, J., et al., 2017, Nat. Methods, 14, 71–73. ↩
-
Darden, T., et al., 1993, J. Chem. Phys., 98, 10089–10092. ↩
-
Ryckaert, J. P., et al., 1977, J. Comput. Phys., 23, 327–341. ↩
-
Andersen, H. C., 1983, J. Comp. Phys., 52, 24–34. ↩
-
Miyamoto, S., Kollman, P. A., 1992, J. Comput. Chem., 13, 952–962. ↩
-
Bussi, G., et al., 2007, J. Chem. Phys., 126, 014101. ↩
-
Bussi, G., et al., 2009, J. Chem. Phys., 130, 074101. ↩
-
Tuckerman, M., et al., 1992, J. Chem. Phys., 97, 1990–2001. ↩